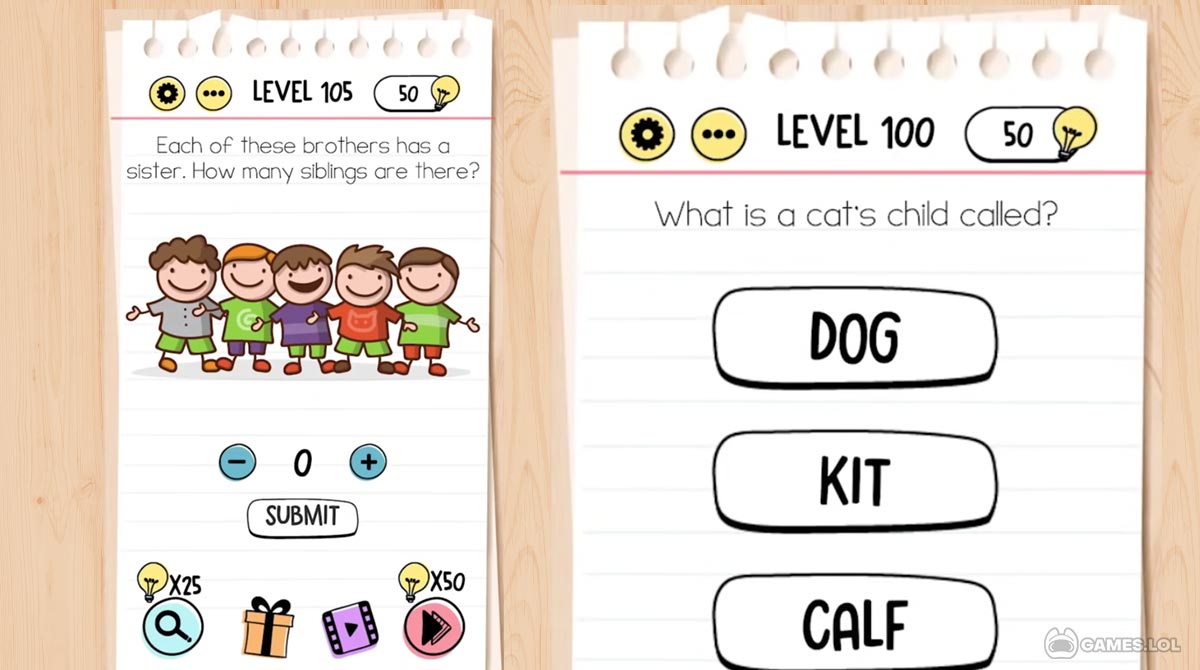
Brain Test Tricky Puzzles: The Mind-Bending Logic Behind Pulquer Challenges
Brain Test Tricky Puzzles: The Mind-Bending Logic Behind Pulquer Challenges
In an age dominated by digital distractions, Brain Test tricks have surged in popularity as a sharp mental workout, blending logic, wordplay, and visual deception to puzzle even the sharpest minds. These brain teasers—popularized through dedicated apps, social media feeds, and puzzle communities—transform mundane imagery into complex cognitive challenges that demand patience, creativity, and meticulous observation. What makes Brain Test puzzles particularly compelling isn’t merely their brain-teasing nature, but the way they expose gaps in intuitive reasoning, forcing solvees to question assumptions and reframe problems in unexpected ways.
At the heart of Brain Test’s enduring allure lies a fusion of psychology and playful illusion. Each puzzle is crafted to exploit cognitive shortcuts—what psychologists call "heuristics"—that guide quick conclusions but often mislead in nuanced situations. “Tricky Brain Test puzzles don’t just test memory or logic alone,” explains Dr.
Elena Marquez, a cognitive scientist specializing in problem-solving behavior. “They expose the hidden friction between what we assume and what is actually true. Success often comes not from raw intellect, but from unlearning mental habits.”
True to form, Brain Test riddles often rely on subtle visual shifts, double meanings, or paradoxical scenarios that redirect perception.
A classic example is the puzzle involving the phrase: “This statement is false.” While logically unstable, such riddles train the mind to detect inconsistencies and avoid black-and-white thinking. Another common motif uses orthogonal constraints—such as “Find three objects you cannot touch with the same hand”—forcing solvers to escape literal interpretations and embrace abstract relationships.
Core Mechanisms That Make Brain Tests Tricky
Brain Test puzzles leverage several deliberate cognitive mechanisms designed to disrupt routine thought patterns: - **Misdirection Through Visual Complexity**: Many puzzles embed distractors within rich, layered imagery.A seemingly simple scene may hide critical clues in plain sight, requiring intense focus and selective attention. As puzzle designer Lars Johansson notes, “The eye skims, but the mind must dig deeper. Often, the key lies not where you look, but where you *don’t* expect it.” - **Ambiguous Language and Double Entendres**: Wordplay is central.
Phrases are constructed to have dual meanings, confusing insiders with their layered definitions. “I speak without a mouth and hear without ears,” the famous riddle goes—its answer, “an echo,” hinges on interpreting metaphor beyond literal function. - **Paradoxical Constraints**: Impossible-seeming conditions anchor several challenges.
For example: “You must carry all four items using only one hand.” Solving such problems demands reframing physical limitations as creative parameters, not barriers. - **Temporal or Sequential Logic Shifts**: Some puzzles embed chronological traps, requiring solvers to track actions across invisible timeframes. This trains not just spatial reasoning, but temporal awareness.
The success of Brain Test puzzles isn’t accidental; each is calibrated through iterative testing, ensuring difficulty scales appropriately while maximizing cognitive engagement. Developers goal on striking a balance between frustration and insight—puzzles too easy dissolve attention, while those excessively obscure breed disengagement. The best Brain Test challenges reside in that sweet spot, where stumbling through confusion cultivates eventual clarity.
Beyond the screen, the value of Brain Test tricks extends into education, occupational training, and therapeutic applications.
Cognitive trainers use incremental puzzle sequences to enhance executive function, while educators integrate Brain Test-style challenges to boost critical thinking in students. Therapists observe improved problem-solving resilience in patients confronting mental rigidity through structured puzzle-solving. Case Study: The “5 Watchmakers” Riddle
One enduring Brain Test classic offers a vivid illustration of these dynamics: “Five watchmakers enter a room and find five watches.
Each says, ‘My watch keeps perfect time.’ Yet only one watch is functioning. How can this be?” The answer—“Each watch was stopped at a different time, yet each knows its own time is correct”—relies on recognizing egocentric perspective and the distinction between accuracy and functionality. This puzzle, widely shared and solved in forums, exemplifies how visual framing misleads reason, demanding a shift from literal to logical interpretation.
The prevalence of Brain Test puzzles today reflects a broader cultural hunger for mental agility amid information overload. These challenges function not only as entertainment but as accessible gateways to cognitive empowerment—activating neural pathways linked to insight, creativity, and adaptive thinking. As challenging as they appear, they ultimately reward quiet persistence and intellectual flexibility.
Solutions often emerge not from brute-force logic, but from subtle shifts in viewpoint—mirroring real-life problems where redefining the question yields extraordinary answers. In sum, Brain Test tricky puzzles are more than fleeting curiosities; they are microcosms of human cognition, revealing how we construct meaning, confront ambiguity, and unlock insight when conventional logic falters. Whether shared casually or studied deliberately, they sharpen minds, one perplexing prompt at a time.


Related Post
Inside Swinging Monkey: How Apple’s Boldest Page-Turner Redefined Interactive Brand Storytelling

Iran SS Anime Strike: Unraveling the Cultural Phenomenon Shaping a New Generation

What Channel Is The Penn State Game On? Breaking Down Media Access in Real Time

Cwag Evolution: How Data Automation Is Reshaping Decision-Making in a Hyperconnected World

