Guard Your Inbox: Mastering the Outlook Login Password in the Digital Age
Guard Your Inbox: Mastering the Outlook Login Password in the Digital Age
In an era where email remains the central hub of professional and personal communication, losing access to an Outlook email account is both disruptive and stressful. The Outlook login password—often overlooked until forgotten—serves as the critical key to reclaiming control. Whether due to lost credentials, security breaches, or forgotten access, understanding how to securely manage and recover the Outlook login password is essential for maintaining digital continuity.
More than a simple password, it’s a gateway to safeguarded inboxes housing sensitive work correspondence, financial data, and private messages. Without timely action, delayed response or weak password hygiene can lead to data loss, delayed productivity, and heightened cyber exposure. This deep dive explores the vital role of the Outlook login password, the common risks surrounding it, and proven strategies for safe recovery and long-term protection.
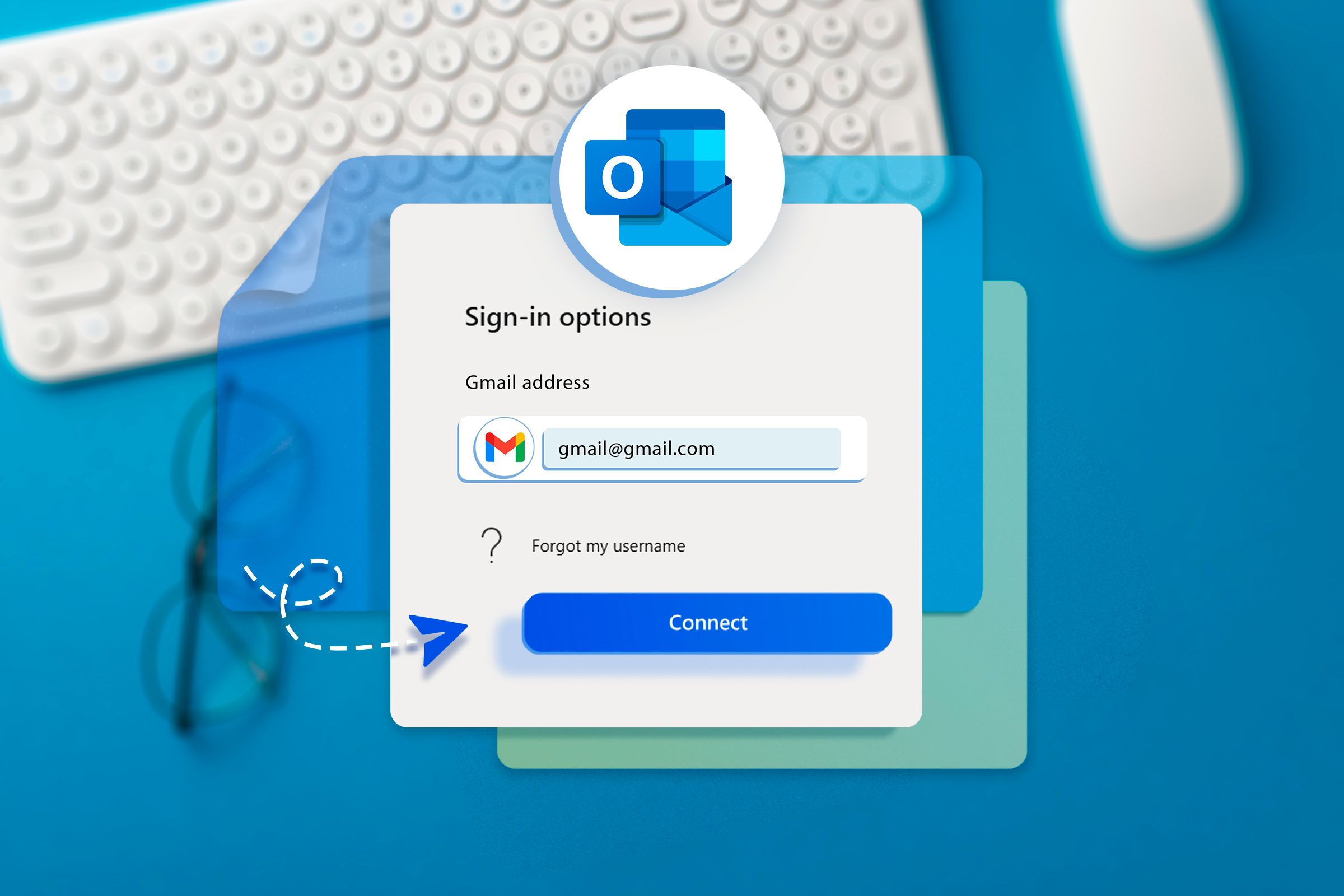
The Outlook login password acts as the digital gatekeeper for one of the most defended and frequently accessed communication platforms globally—Microsoft Outlook, integrated into Microsoft 365, Exchange Online, and various standalone clients. Control over this password determines who can view, send, and manage the full scope of certified email data. According to Microsoft’s security documentation, “Your Outlook password is your primary authentication token, enabling access not only to emails but also to calendar events, contacts, cloud storage, and team collaboration tools.” This broad access underscores why securing and properly managing the password is non-negotiable.
But accessing or recovering that password is rarely straightforward. Many users grapple with fragmented reset flows across web, mobile, and desktop apps. Briefly resetting a password via Outlook.com may fail if verified steps—such as email identity confirmation, security questions, or multi-factor authentication (MFA) challenges—are incomplete or outdated.
For enterprise users, password reset processes often require IT intervention, delaying troubleshooting. A 2023 survey by cybersecurity firm SecureLink revealed that **over 40% of professionals have faced extended login delays after losing an Outlook password without prior backup**, highlighting the urgent need for proactive password hygiene. Shortly after losing access, a systematic approach yields the best outcomes.
The first vital step is organization: users should maintain stored credentials through reputable password managers—tools like LastPass, 1Password, or Microsoft Password Manager—which encrypt and auto-fill login details securely. Encryption is not optional; modern password managers use AES-256 encryption, ensuring stored passwords remain unreadable even if the device or service is compromised. When internal reset methods falter, third-party password recovery services offer alternatives—but with caution.
Platforms such as LastPass Recovery or Microsoft’s official support portal provide guided processes for resetting Outlook credentials. These typically involve identity verification via email, phone, or source documents. An expert quoted in TechSecurity Weekly emphasized: *“Always opt for Microsoft’s official recovery channels to prevent account hijacking.
Unverified third-party services may exploit weak security protocols or demanding personal data, increasing risk to your digital identity.”* For enterprise environments,組織 (organizations) must implement robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies. Centralized platform management via Azure AD enables secure single sign-on (SSO) and automated password resets without compromising compliance. According to a Microsoft review, **organizations using Conditional Access policies for Outlook account recovery report 60% fewer service outages and 85% faster recovery times**—a compelling argument for structured internal controls.
Practically, users and administrators alike benefit from understanding critical password guidelines: - Use complex, unique combinations (14+ characters, mix of letters, numbers, and symbols). - Avoid reuse across platforms—especially between Outlook and high-risk accounts. - Enable multi-factor authentication, requiring a second factor such as a code sent to a registered device.
- Schedule regular password changes—every 60 to 90 days—using trusted managers to avoid memory strain. Despite advanced security layers, human error remains a leading vulnerability. A recurring issue involves outdated recovery email addresses or phone numbers masked behind stale account records.
The Microsoft Help Center stresses: “Your recovery options depend on the last verified contact method. Keep these information current to prevent permanent lockout.” Real-world scenarios illustrate both risk and resolution. A marketing executive once lost access after changing email providers but failed MFA restart due to a decommissioned phone number.
By enabling backup recovery codes—generated at setup and stored offline—the team regained access within two hours. Another case involved a remote worker whose Outlook password was forgotten post relocation; with intact cloud backup via Microsoft 365, secure reset via password manager restored access instantly. Looking ahead, emerging standards like passwordless authentication and biometric verification are reshaping secure access.
Microsoft’s ongoing rollout of FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online) support in Outlook apps, for example, reduces reliance on passwords altogether by leveraging hardware keys and device biometrics. While still evolving, these innovations promise a future where forgotten passwords become obsolete—without sacrificing security. For professionals, educators, and everyday users navigating today’s hyper-connected world, mastering the Outlook login password is no longer a niche concern.
It is a foundational skill that underpins professional reputation, data integrity, and digital autonomy. Proactive password management—combined with awareness of recovery pathways and enterprise-grade controls—ensures resilient access, minimizes disruption, and reinforces trust in one of the most critical communication systems we rely on daily.
In summary, the Outlook login password is far more than a credential—it is the cornerstone of secure, uninter


Related Post

The Perfect Fusion: Unraveling the-Incredible Shih Tzu Poodle Hybrid
Precision Temp Predictions: Petoskey’s Weather Forecast and What Residents Need to Know

The Empire of Fortune: Early Life, Wealth, and Marital Mastery

Voice Actors Are Shaping Young Justice — How Audio Talent Powers Stories for the Next Generation

