Mastering the Law of Cosines: Unlock Angle Secrets in Every Triangle
Mastering the Law of Cosines: Unlock Angle Secrets in Every Triangle
In a world where precision defines success—from architecture to space exploration—the Law of Cosines stands as a cornerstone of geometric computation. This powerful formula extends the Pythagorean theorem to non-right triangles, enabling exact calculations of unknown angles and side lengths when traditional methods fall short. By bridging the gap between sides and angles, the Law of Cosines empowers engineers, navigators, and physicists with a reliable tool to navigate the complexities of irregular triangles.
The Law of Cosines: A Geometric Powerhouse
While right triangles lend themselves easily to the familiar Pythagorean theorem, most triangles encountered in real-world applications carry angles that defy simplicity.
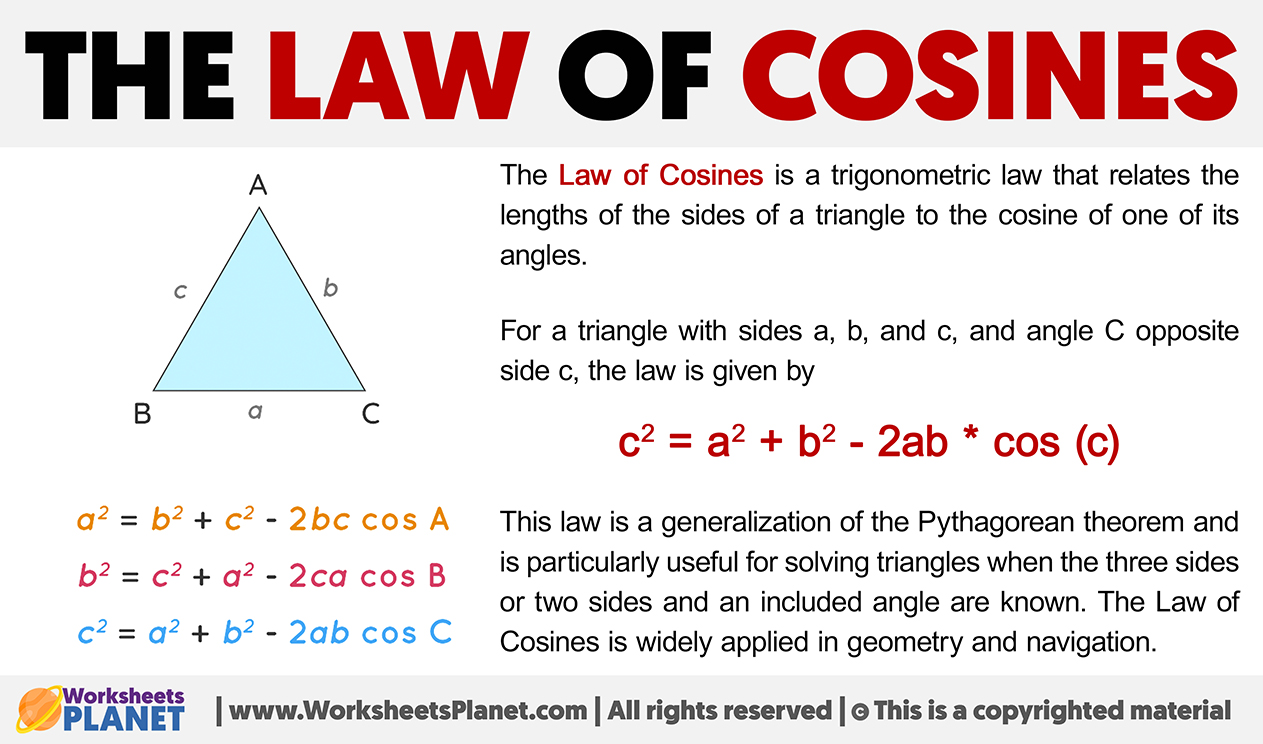
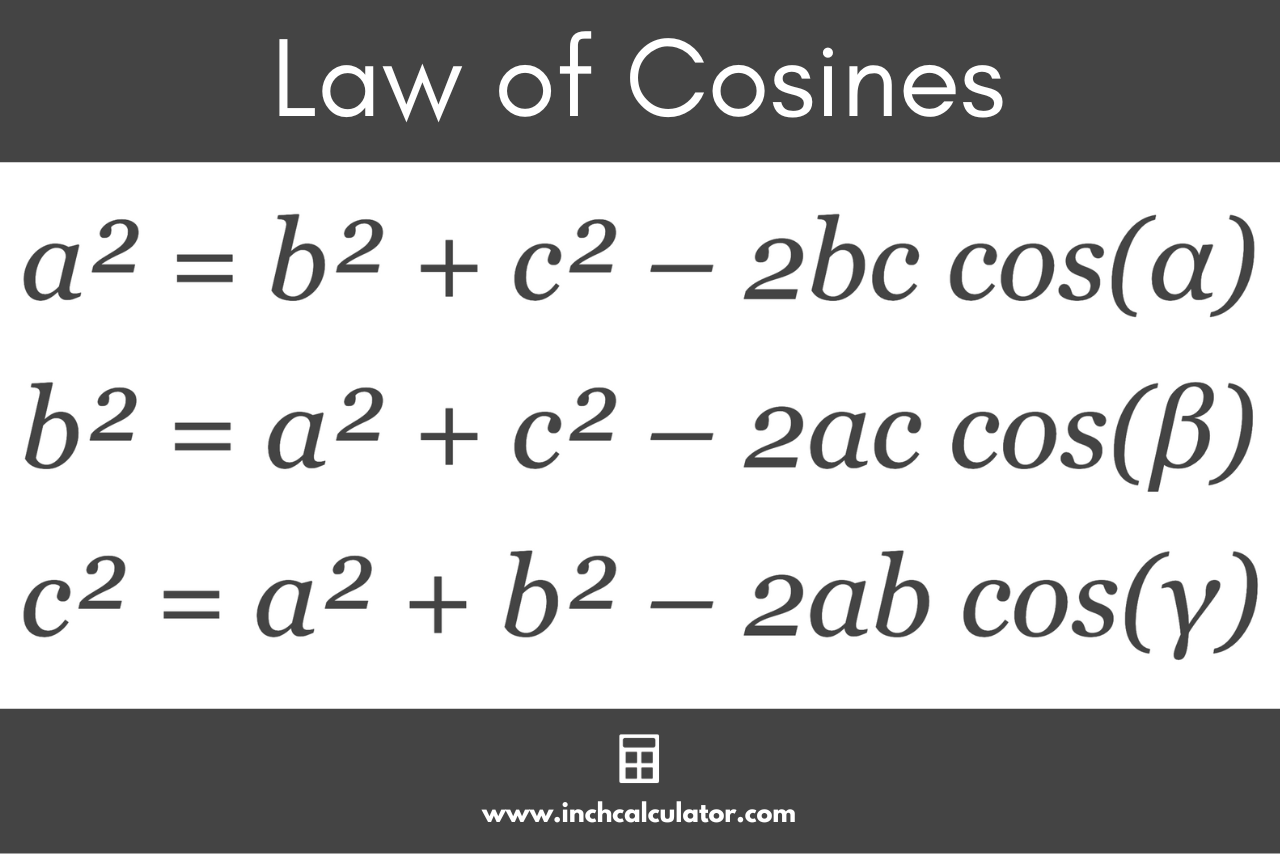
The Law of Cosines fills this gap, offering a robust formula applicable to any triangle—whether acute, obtuse, or right-angled. Derived from fundamental principles of trigonometry and vector geometry, it expresses the square of one side in terms of the other two sides and the cosine of the included angle. This adaptability makes it indispensable for solving triangles where only side lengths or two sides and the included angle are known.
String mathematically, the Law of Cosines states: c² = a² + b² – 2ab cos(C), where c is the side opposite angle C, and a and b are the other two sides.The inclusion of the cosine term transforms an equilateral triangle into a solvable equation, turning ambiguity into precision. Unlike sine-based laws that require cumulative angle proposals post-solve, the Law of Cosines delivers direct results in one step when the angle itself is defined by its adjacent sides.
Understanding the Formula: A Closer Look at Its Mechanics
At first glance, the formula may appear complex, but each component plays a precise role. The squared terms (a², b²) represent known side lengths forming the angle, encapsulating spatial magnitude.
The product 2ab scales with the cosine of angle C, adjusting for how much the angle deviates from 90°—a critical correction absent in right-triangle trigonometry. When angle C measures greater than 90°, the cosine turns negative, subtracting from the sum and reflecting increased side length due to overshoot. Conversely, acute angles reduce the adjustment, yielding shorter projected lengths.
This is not merely algebraic manipulation—it reflects physical reality.
In dynamic systems, such as determining a drone’s extendable arm angle relative to its base, the Law of Cosines computes the exact tension force distribution by resolving forces through angular geometry. The formula turns vectors and distances into actionable data, closing the gap between measurement and decision.
Applications Across Disciplines: From Classroom to Canopy
The reach of the Law of Cosines extends far beyond theoretical geometry. In navigation, mariners and pilots use it to triangulate positions when GPS signals fade, calculating distances and bearings from known landmarks.
Architects apply it to design complex rooflines and cantilevered structures where equal or irregular supports demand precise angular alignment. Surveyors rely on it to map terrains across valleys and hills, ensuring boundary lines reflect actual ground spreads.
Astronomy also depends heavily on this formula. When measuring vast distances between stars or planets, indirect methods such as parallax yield side lengths and angular separations—both amenable to the Law of Cosines.
With these inputs, scientists compute celestial distances with remarkable accuracy, illustrating how foundational math enables cosmic-scale insight. Even in mechanical engineering, gear teeth profiles and linkage mechanisms demand angle-side relationships verified by this law, demonstrating its embedded role in design logic.
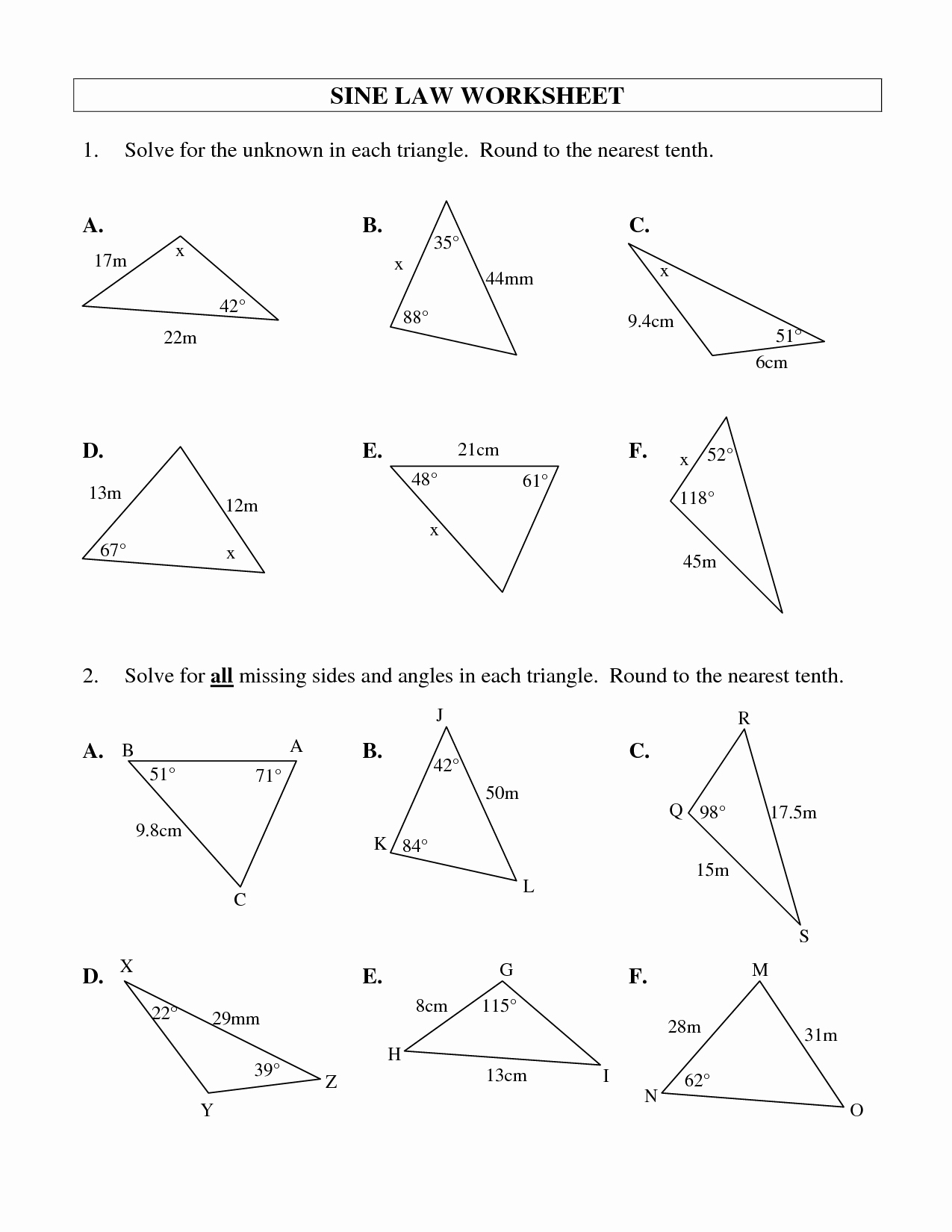
Step-by-Step: Solving a Triangle with the Law of Cosines
To practice the formula, consider a triangle with sides a = 7 cm, b = 10 cm, and included angle C = 40°. The goal: find side c.
The formula becomes: c² = 7² + 10² – 2(7)(10)cos(40°) c² = 49 + 100 – 140 × cos(40°) Using cos(40°) ≈ 0.766 c² ≈ 149 – 107.24 = 41.76 c ≈ √41.76 ≈ 6.46 cm
This workflow highlights the formula’s clarity. Input knowns, identify the included angle, compute cosine, substitute, and solve—either algebraically or via calculator. When angle C exceeds 90°, say C = 120°, cos(120°) = –0.5, flipping the sign and amplifying the side length effect.
Such nuances underscore why understanding angle orientation matters.
Cautions and Common Pitfalls in Using the Law
Despite its power, misuse of the Law of Cosines can lead to errors. A frequent mistake is misassigning sides or angles—placing the cosine opposite the correct adjacent pair invalidates the result. Equally, arithmetic oversights—like miscalculating cosine values or squaring errors—compound quickly.
A small miscalculation in cos(160°) versus cos(40°) drastically alters side length. Furthermore, relying on this formula for right triangles is unnecessary; the Pythagorean theorem suffices there, preserving computational efficiency.
A critical pitfall lies in ignoring unit consistency. Whether sides are measured in meters, centimeters, or arbitrary units, the cosine function demands angle consistency—typically in degrees or radians—not chemical units.
Cross-checking results with alternative methods, such as the Law of Sines in complementary scenarios, strengthens confidence in the solution.
The Mathematical Essence: Precision Through Cosine
At its core, the Law of Cosines embodies a geometric truth: the cosine of an angle encodes orientation, translating angular deviation into measurable side adjustments. This fusion of arithmetic and spatial logic elevates it beyond calculation—it becomes a language for describing three-dimensional space. Whether resolving forces, plotting courses, or scaling models, the formula reframes ambiguity as quantifiable data.
Mathematicians often emphasize its symmetry
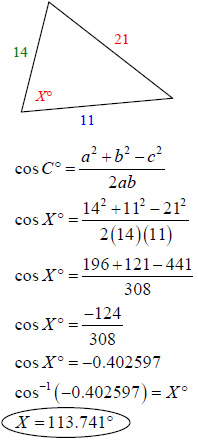
Related Post

Discover the Best Salones De Fiesta Near Me: Where Celebration Meets Style

King Vons Found Dead: Xxl Records’ Statement Triggers Outpouring Over Autopsy Imagery and Legacy

Gabriela Sabatini Partner: Exploring The Life And Relationships Of A Tennis Legend

Bo Nickal’s Boxtrack Rounddown: Next Fight Set to Redefine Muay Thai’s Bo Nickal Era

