The Hidden Architects: Understanding the Vital Function of Reticular Tissue in the Human Body
The Hidden Architects: Understanding the Vital Function of Reticular Tissue in the Human Body
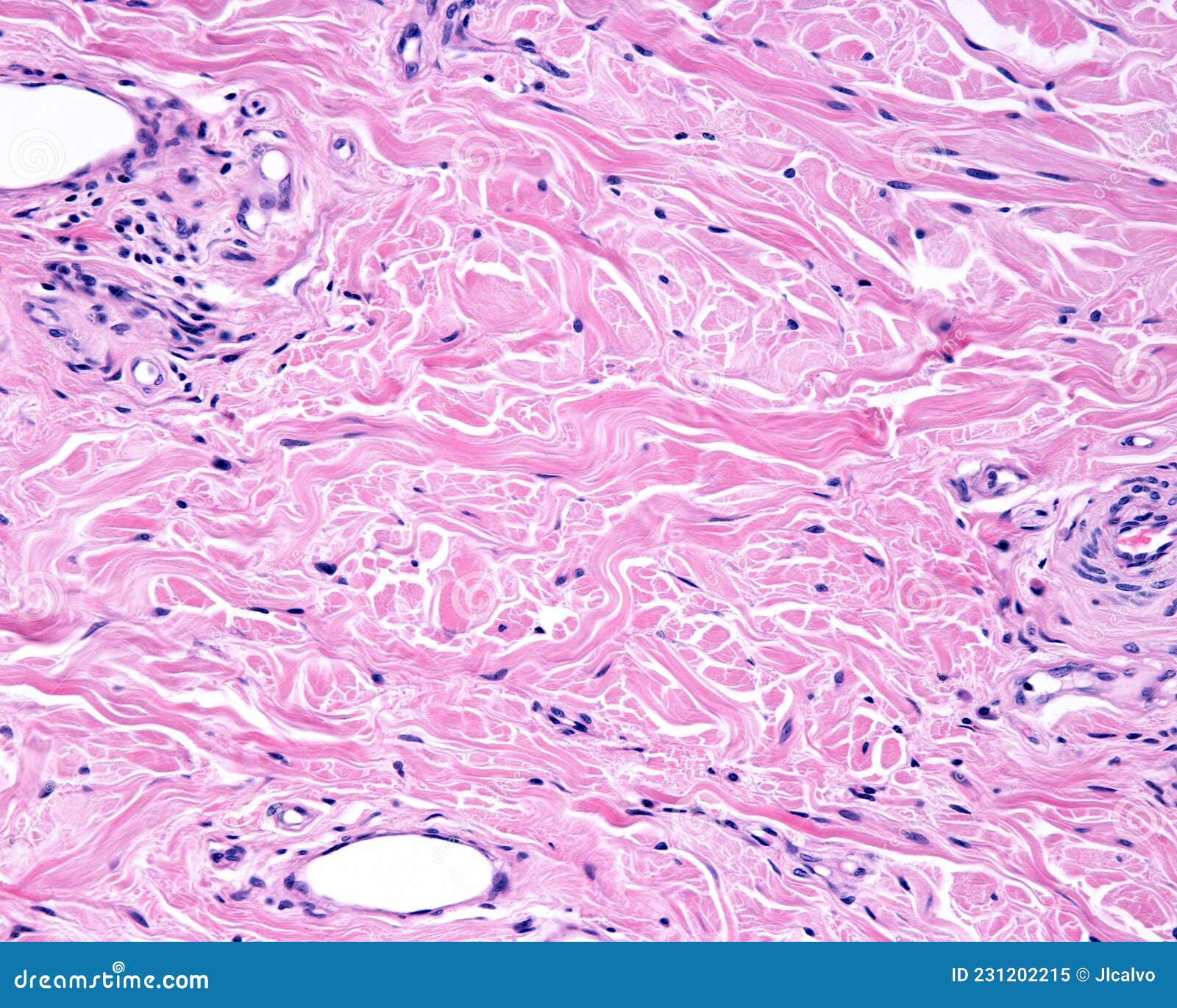
Reticular tissue forms the unsung backbone of internal organs, weaving an intricate network that supports structural integrity, regulates fluid movement, and enables efficient immune surveillance. More than a mere connective framework, this specialized reticulin-based scaffold serves as both a mechanical mesh and a dynamic biological conductor in vital physiological processes. From filtering blood in the spleen to sustaining the respiratory architecture of the lungs, reticular tissue quietly enables life-sustaining functions that remain underappreciated in general discourse.
At its core, reticular tissue is composed primarily of fine, network-like fibers made of reticular collagen and special glycoproteins called reticular fibers. These threads form a delicate yet robust mesh — zoom in microscopically, and what emerges is a three-dimensional lattice that defines the microenvironment of organs like the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and lungs. As Dr.
Elena Martinez, a histopathologist at the National Institute of Biomedical Research, explains: “Reticular tissue isn’t just passive scaffolding; it actively shapes organ architecture, guides cell migration, and maintains the delicate balance between filtration, drainage, and immune response.” This dynamic structure supports hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow, enabling blood cell production, while also facilitating the rapid exchange of nutrients and immune cells in lymph organs.
Structural Support and Architectural Precision
The primary role of reticular tissue lies in providing structural framework — a flexible yet durable template that maintains organ shape and internal compartmentalization. Unlike dense fibrous connective tissue that reinforces joints or skin, reticular tissue forms a porous, branching mesh that allows fluid flow and cellular diffusion.In the spleen, for example, its dense reticular network creates the red pulp’s sinusoids — narrow channels lined with macrophages and storage macrophages — where old red blood cells are filtered and iron is recycled. Meanwhile, in the liver, specialized reticular fibers anchor chordate stromal cells, forming the sinusoidal framework essential for blood purification.
This architectural precision extends to respiratory function.
The lung’s alveolar septa are reinforced with a reticular network that maintains airspace stability while enabling vascular coaptation. As researcher Dr. Raj Patel notes, “Without this reticular scaffold, the delicate alveolar walls would collapse, impairing gas exchange and threatening respiratory homeostasis.” Reticular tissue thus ensures organs retain function under dynamic physiological stress, preventing structural degradation during blood flow, breathing, and immune activation.
Dynamic Regulation of Fluid Exchange and Immune Surveillance
Beyond mere support, reticular tissue plays a critical role in fluid dynamics and immune coordination. Its open, honeycombed architecture facilitates wide interstitial spaces where plasma proteins, immune cells, and signaling molecules circulate freely. This permeability enables lymphoid organs like lymph nodes to efficiently trap pathogens and mount rapid immune responses.The reticular weave acts as a sieve — allowing immune cells passage while retaining larger debris — optimizing surveillance without compromising filtration efficiency.
In bone marrow, reticular cells form a supportive niche for hematopoietic stem cells, secreting cytokines that direct blood cell development. “The reticular microenvironment isn’t just a passive container,” explains Dr.
Martinez. “It actively communicates with developing cells, influencing lineage commitment and ensuring proper immune cell production.” This functional specificity underscores reticular tissue’s role as a bioactive participant in homeostasis, blurring traditional boundaries between connective tissue and active physiological regulation.
Hematopoietic Niche and Stem Cell Maintenance
One of reticular tissue’s most sophisticated functions lies in anchoring the hematopoietic niche — a specialized microenvironment where blood cell formation occurs.Reticular stromal cells secrete key growth factors like stem cell factor (SCF) and interleukin-3 (IL-3), fostering the dormancy and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. Disruption of this network — as seen in radiation therapy or bone marrow failure — leads to diminished blood cell output, illustrating the tissue’s indispensable role in regeneration.
Clinical Implications and Diagnostic Significance
Clinically, reticular tissue integrity is a diagnostic marker in multiple diseases.In fibrosis, excessive reticular deposition stiffens organs, impairing function — common in cirrhosis and pulmonary fibrosis. Conversely, reticular breakdown signals tissue damage, observable in conditions like chronic lymphadenitis or lymphomas, where the scaffold collapses, compromising immune function. Imaging techniques targeting reticular architecture, such as high-resolution MRI or elastography, are increasingly valuable in early disease detection.
A Master regulator in Health and Disease
Reticular tissue exemplifies the convergence of structure, function, and dynamic response in human biology. Far from inert connective support, it orchestrates blood filtration, immune surveillance, and cellular development with remarkable precision. Its role extends beyond anatomy — influencing regeneration, disease progression, and therapeutic outcomes.As medical imaging and regenerative therapies advance, understanding this enigmatic tissue promises new insights into organ function and healing. In the intricate machinery of the body, reticular tissue quietly holds the key, proving that sometimes, the most powerful biological systems are rooted in subtle, sophisticated design.



Related Post

The Five Jessica Files: Uncovering the Powerhouse Behind Fox News’ Most Influential Voices

Unveiling The Life And Career Of Isaiah Stannard: From Humble Beginnings to Pioneering Influence

The Hidden Science Behind PDFs: Unlocking Their Full Potential Through Advanced Technologies

Kour Io Poki: The High-Stakes Game That Redefined Filipino Gaming Culture

