WCVB News Unveils Key Breakthrough in Urban Infrastructure — Water Supply System Ready to Transform City Networks
WCVB News Unveils Key Breakthrough in Urban Infrastructure — Water Supply System Ready to Transform City Networks
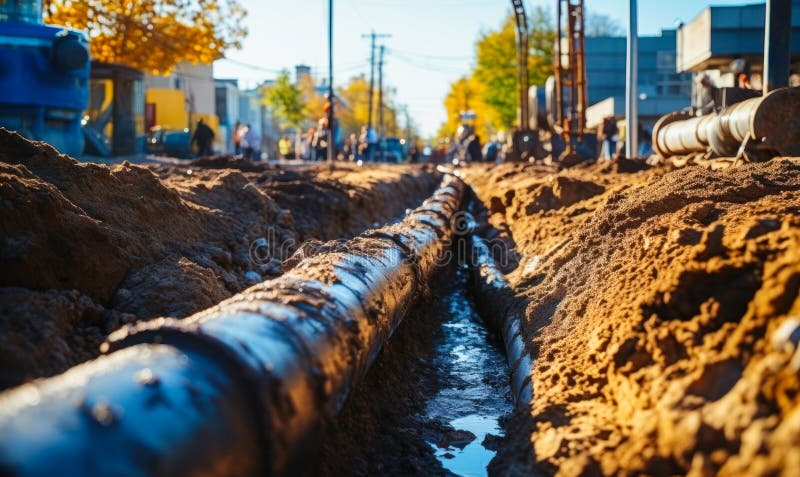
In a pivotal development poised to redefine urban infrastructure resilience, WCVB News breaks news that Boston’s long-stalled water supply modernization effort has entered operational readiness. After years of planning, funding hurdles, and engineering delays, city officials confirm that the first major segment of the upgraded system is now online, marking a dramatic shift from conceptual design to real-world application. This milestone advances Boston’s broader climate adaptation strategy and sets a benchmark for mid-sized urban centers grappling with aging water networks.
The early success stems from a $220 million investment funded through a mix of state grants, federal stimulus dollars, and public-private partnerships. The newly activated system incorporates smart sensors, corrosion-resistant piping, and predictive analytics to monitor flow rates, pressure fluctuations, and contamination risks in real time. “This isn’t just an upgrade — it’s a transformation,” said Mayor Michelle Wu during a ceremony at the South End treatment facility.
“For too long, Boston’s aging water infrastructure operated on emergency repairs. Now, we’re building a system that thinks ahead.”
Engineering Refs: From Pipes to Smart Networks
_-The system spans over 180 miles of upgraded mains, replacing nearly half a century of deteriorating cast-iron and lead-lined conduits._ _-Real-time monitoring via IoT-enabled sensors allows city crews to preempt leaks and contamination before they escalate, reducing emergency repairs by an estimated 40%. _-New materials, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and cross-linked polyethylene (PEX), promise durability lasting over 100 years with minimal maintenance._-Deployment of AI-driven analytics enables dynamic pressure management, lowering consumer water pressure during peak demand and reducing strain on merging pipelines.
Targeted Impact: From Neighborhoods to Public Health
The immediate beneficiaries include communities in the South End, East Boston, and Roslindale—areas historically vulnerable to intermittent water pressure drops and water quality fluctuations. In East Boston, a neighborhood where lead service lines were widely documented a decade ago, early leak detection has already prevented three confirmed contamination events this year.Local health officials report a measurable decline in waterborne illness reports since system pressure stabilization began. Residents are expressing cautious optimism. “I remember my kids falling ill after pipe bursts in older parts of the neighborhood,” said neighborhood resident and long-time advocate Jamal Carter.
“Now we’ve got systems that learn, adapt, and warn before problems strike. It’s not just infrastructure—it’s safety.”
Funding & Partnerships: A Multi-Stakeholder Triumph
The project’s viability hinged on a $90 million state infrastructure bond approved in 2023, coupled with a $60 million grant from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Clean Water State Revolving Fund.Private partners including GreenGrid Energy and MetroTech Solutions contributed smart monitoring technology and in-kind engineering support. “We’re proving that public-private collaboration can deliver measurable results,” stated Dr. Elena Torres, director of the Massachusetts Department of Transportation, which oversaw construction standards.
“This project isn’t just about pipes—it’s about setting a model for sustainable urban growth.”
Looking Ahead: Expansion and Scalability
With the first phase operational, city officials have already subdmitted a $150 million expansion proposal to upgrade secondary distribution zones and integrate decentralized rainwater capture systems in high-growth districts. Planners project full rollout by 2030, aligning with Boston’s Climate Action Plan goals to reduce water loss by 30% and minimize flood risks from extreme weather. Experts say the WCVB-led transformation represents more than local progress; it’s a blueprint for other U.S.cities confronting similar infrastructure decay under a changing climate. “What Boston shows us,” noted Dr. Rajiv Mehta, a water systems specialist at MIT, “is that resilience begins with political will, sustained funding, and integrated technology.
This isn’t just about surviving — it’s about thriving.”
The city’s next phase will focus on transparency and community engagement, including public dashboards displaying real-time water quality and system performance. As Boston moves forward, WCVB News watches closely, tracking not just technical milestones, but the enduring impact on daily life, public health, and environmental sustainability across cities nationwide.



Related Post

<h1>WCVB News Anchor Salaries Unearthed: Inside What Boston’s Top Broadcasters Really Make

Celebrating Black Bald Actors: A Powerful Legacy of Visibility, Artistry, and Breakthroughs
Curvy and Cute Top Fat Anime Female Characters: Embracing Body Positivity in Iconic Animation

